Agricultural project planning follows a structured process called the project cycle, which consists of various steps to ensure that projects are effectively designed, implemented, and meet the needs of the target communities or sectors. Two key stages in this process are need assessment and problem identification, both of which are crucial for understanding and addressing the issues that the project aims to solve. Below is an overview of the project cycle, with a focus on these important early stages.
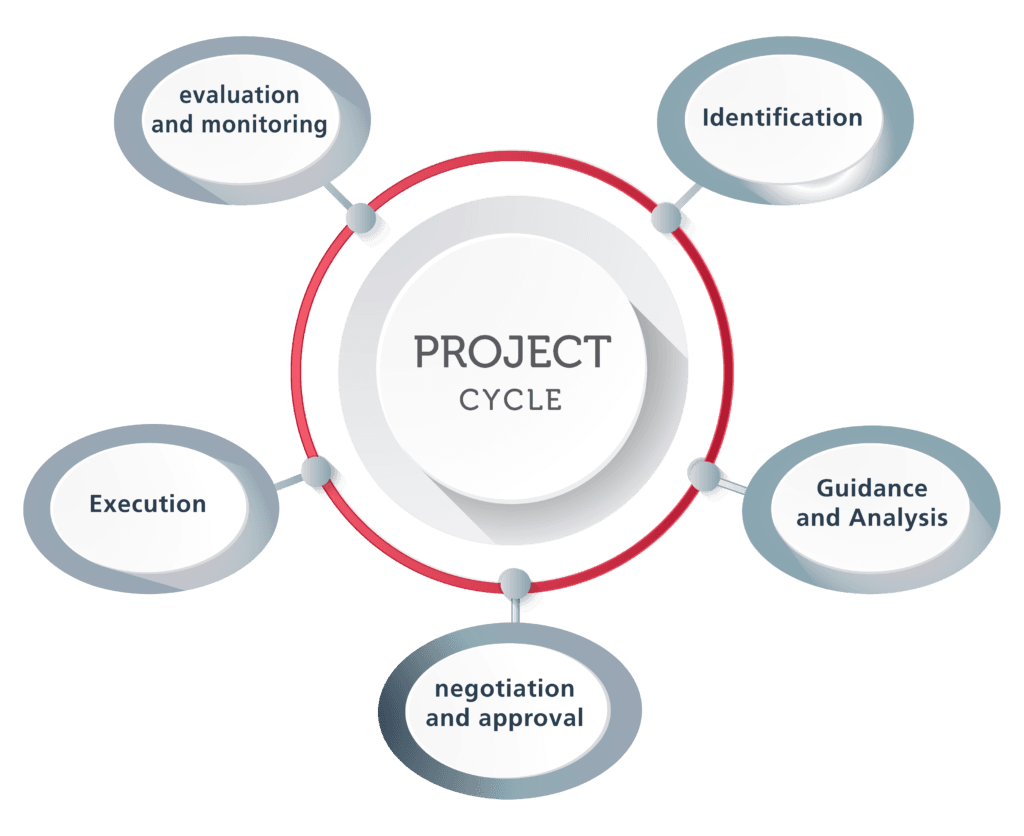
Table of Contents
Overview of the Project Cycle
The project cycle outlines the step-by-step approach to planning, executing, and evaluating a project. This process ensures that agricultural projects are designed to solve real problems, implemented efficiently, and lead to meaningful outcomes. The key stages of the project cycle include:
Project Identification: The need for a project is recognized based on existing issues or opportunities within the agricultural sector.
Need Assessment/Problem Identification: A thorough analysis is conducted to understand the specific needs and problems of the target area or population, ensuring the project is relevant.
Project Design: The project’s goals, activities, and strategies are formulated based on the identified needs.
Project Appraisal: The project is evaluated for its feasibility, potential impacts, and how well it aligns with larger development goals.
Project Implementation: The project is carried out as planned, with the activities executed on the ground.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Progress is monitored throughout the project, and an evaluation is conducted to assess whether the objectives have been met.
Project Closure and Reflection: The project is concluded, and lessons learned are documented to improve future initiatives.
Among these stages, need assessment and problem identification are critical in shaping the rest of the project’s development.
Need Assessment in Agricultural Projects
Need assessment is a process of gathering and analyzing data to determine the specific challenges or gaps in a community, sector, or region. In the context of agricultural projects, need assessment helps identify the key areas where intervention is required, such as improving farming techniques, water management, or enhancing rural livelihoods.
The importance of need assessment lies in its ability to ensure the project focuses on real issues. It helps avoid assumptions and ensures that the project is based on actual data and input from the community.
Steps in Need Assessment of Project cycle
The steps in need assessment of Project cycle,
Data Collection
Gathering information through surveys, interviews, and field visits to understand the current agricultural practices, resources, and challenges.
Involving Stakeholders
Engaging farmers, local communities, and other relevant parties to get diverse perspectives on the needs and priorities.
Prioritizing Needs
Once data is collected, the needs are ranked based on factors like urgency, impact, and feasibility. This helps focus the project on the most critical challenges.
Example: A need assessment might reveal that farmers in a rural area struggle with low crop yields due to outdated farming techniques and inadequate access to water. These findings would guide the design of a project to address these specific issues.
Problem Identification in Agricultural Projects
Problem identification focuses on pinpointing the specific issues that the project will address. It involves understanding the root causes of these problems, their effects, and how they impact the agricultural community or sector.
This step goes beyond the surface-level symptoms to identify the underlying causes of the problems. For example, if low agricultural productivity is identified, the root causes could include poor soil quality, lack of modern equipment, or insufficient training for farmers.
Steps in Problem Identification
Situation Analysis
A detailed examination of the agricultural environment, considering factors such as economic, social, and environmental conditions.
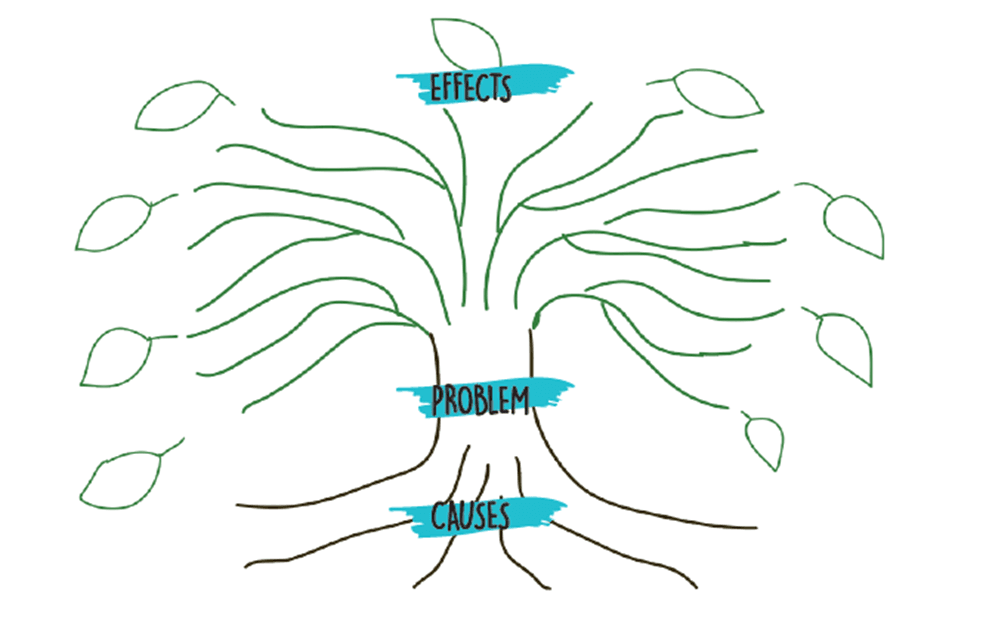
Root Cause Analysis
Identifying the deeper reasons behind the problems. Tools like the “problem tree” can help map out how a central issue is connected to its causes and effects.
Stakeholder Input
Engaging stakeholders to understand the challenges they face and gain insight into the underlying issues affecting their agricultural productivity.
Example: In a region where farmers are facing declining crop yields, problem identification might show that the real issue is poor irrigation infrastructure and a lack of access to improved seeds. Understanding these root causes allows the project to focus on solutions that directly address the real barriers to agricultural success.
How Need Assessment and Problem Identification Influence Project Design
Need assessment and problem identification are essential for shaping an agricultural project that is both relevant and effective. By clearly understanding the community’s needs and the problems they face, the project can be designed with targeted solutions. During the project design phase, clear objectives are set, activities are defined, and necessary resources are allocated.
For example, if the need assessment identifies a lack of modern farming knowledge, the project design might include training programs, technology demonstrations, and access to new tools and techniques. Similarly, if the problem identification highlights poor water management, the project could focus on building new irrigation systems and teaching farmers how to use water efficiently.
Benefits of Proper Need Assessment and Problem Identification
Focused Solutions
The project can address the most urgent and important challenges, ensuring resources are used wisely.
Stakeholder Support
Involving the community from the beginning helps build trust and ensures that the project aligns with their needs and expectations.
Greater Impact
Projects designed with a solid understanding of the problems and needs are more likely to succeed and create lasting improvements in agricultural practices and livelihoods.
Conclusion
The project cycle provides a systematic approach to agricultural project planning, ensuring that projects are well-designed, effectively implemented, and achieve meaningful results. Need assessment and problem identification are crucial early steps that help clarify the challenges to be addressed and provide a foundation for the rest of the project. By conducting thorough need assessments and identifying the root causes of agricultural problems, projects can be designed to create long-lasting positive impacts on rural communities and agricultural productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why is need assessment important in agricultural projects?
Need assessment is important because it helps identify the actual challenges faced by a community, ensuring that the project addresses real issues rather than assumptions. It provides the data needed to design effective solutions, ensuring the project is relevant and impactful.
What is problem identification in agricultural projects?
Problem identification focuses on pinpointing the specific issues the project will address. It involves understanding the root causes of challenges in agriculture and their effects. By identifying these core issues, the project can target the problems directly and more effectively.
What is the project cycle in agricultural planning?
The project cycle in agricultural planning is a structured process that guides the planning, implementation, and evaluation of agricultural projects.
Related Articles

