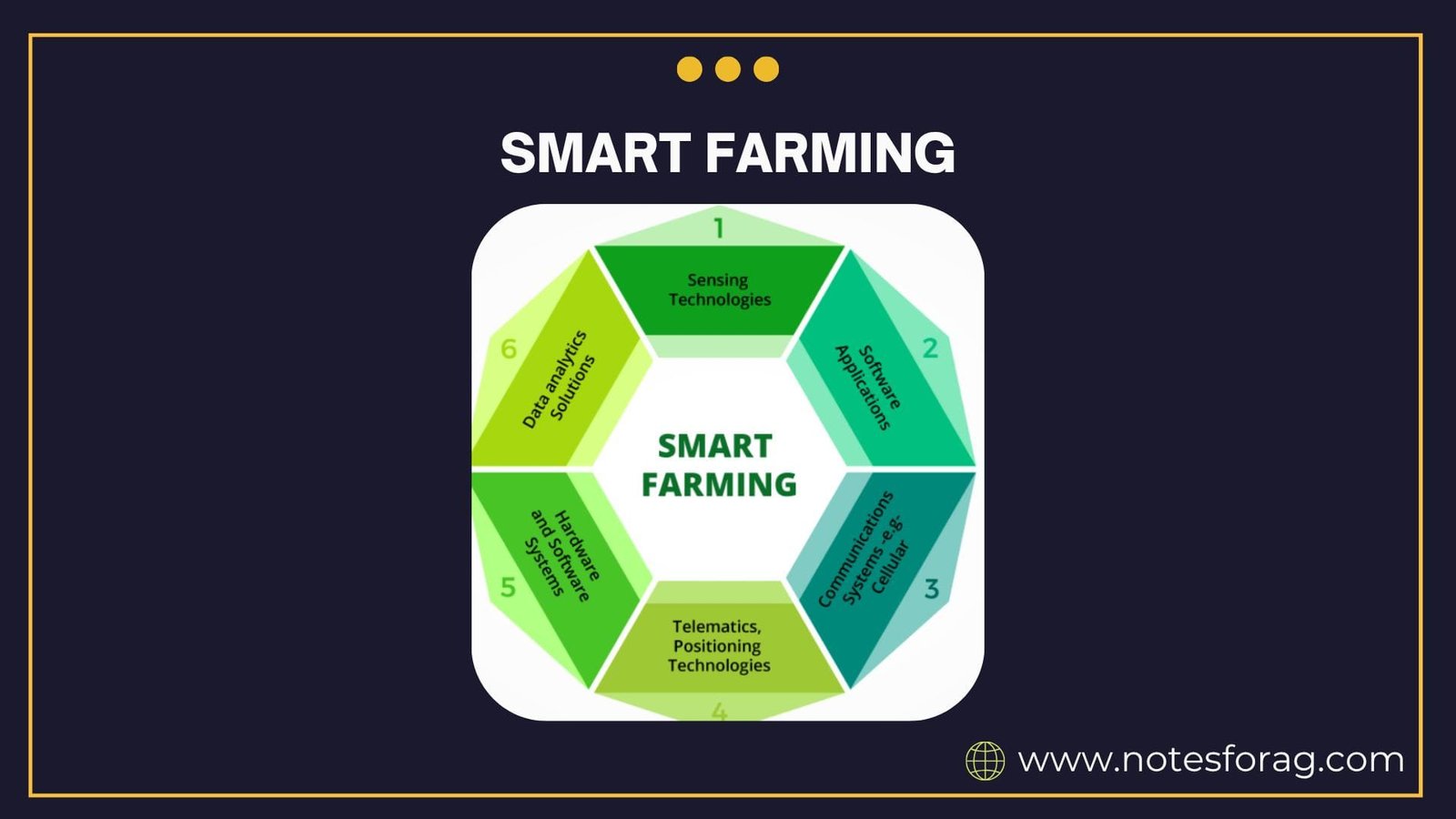
Introduction
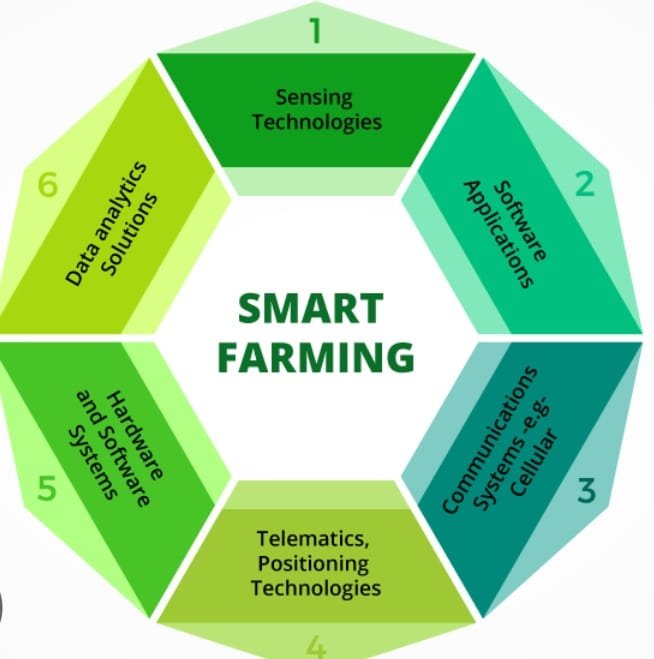
Smart farming, also known as precision agriculture or digital farming, refers to the application of modern technologies and data-driven approaches to agriculture. It uses tools like sensors, GPS, IoT devices, robotics, drones, and data analytics to make farming more efficient, productive, and environmentally friendly. The main goal of smart farming is to optimize the use of resources such as water, fertilizer, and land, while increasing crop yields and reducing waste.
Importance of Smart Farming
Smart farming is important in today’s agricultural world because it addresses key challenges like climate change, labor shortages, and food security. By using smart technologies, farmers can monitor crops and soil in real time, automate tasks, and make better decisions based on accurate data.
Table of Contents
Key Components of Smart Farming
1. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture involves observing, measuring, and responding to crop variability. It uses GPS and mapping software to apply water, fertilizer, and pesticides exactly where needed, which reduces costs and environmental impact.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) in Agriculture
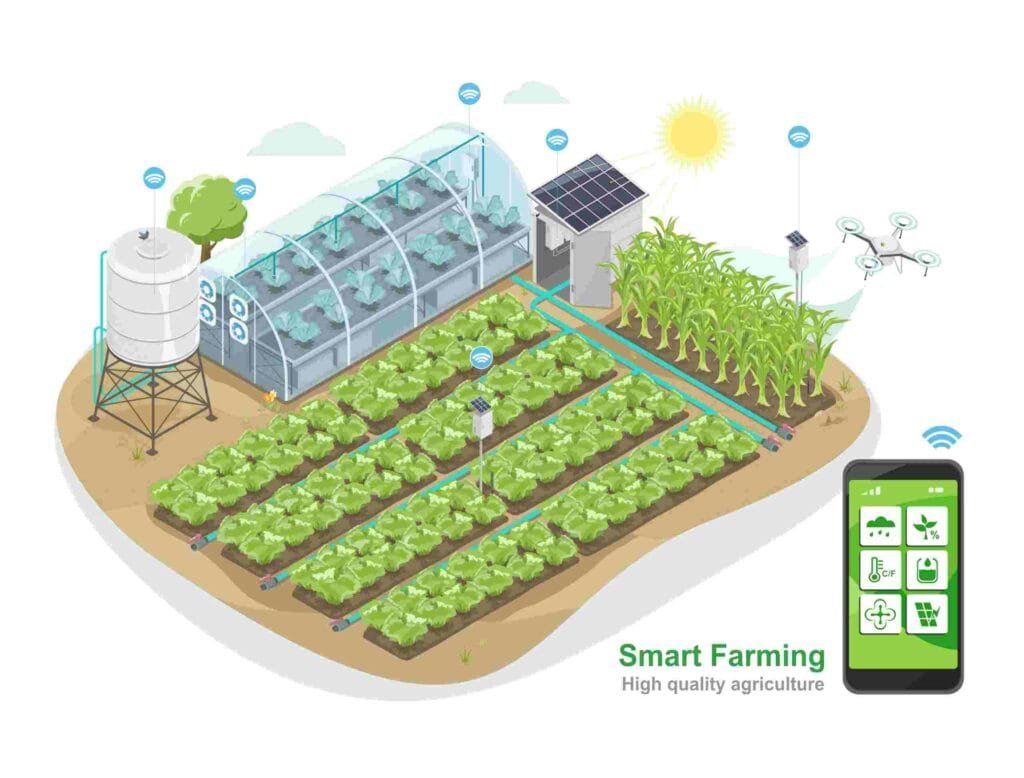
IoT devices like soil moisture sensors, temperature monitors, and weather stations collect data from fields. This data is used to monitor plant health, irrigation needs, and climatic changes.
3. Drones and Aerial Imaging
Drones equipped with cameras and sensors provide aerial images of farms. These images help detect plant diseases, monitor crop health, assess irrigation, and even count livestock.
4. Robotics and Automation
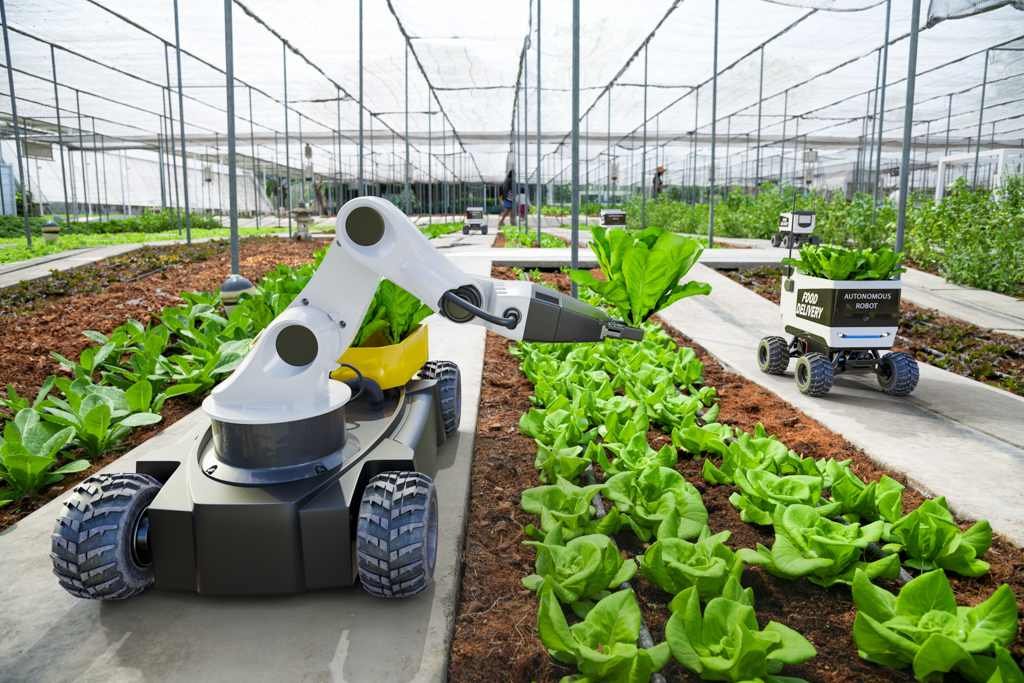

Smart tractors, robotic harvesters, and automated irrigation systems perform tasks like planting, watering, and harvesting with precision and efficiency. This reduces labor costs and human error.
5. Big Data and Analytics
Smart farming generates a large amount of data. Data analytics tools analyze this data to identify patterns, predict yields, and provide recommendations on crop management.
6. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML tools help in predicting weather patterns, pest outbreaks, and disease risks. They also assist in decision-making and improve the accuracy of farm operations.
7. Geographic Information System (GIS)
GIS is used to map fields and analyze spatial data. Farmers can monitor soil conditions, plan planting schedules, and optimize field layouts using GIS data.
Benefits of Smart Farming
1. Increased Productivity
Smart farming increases crop yields by ensuring that each plant receives the right amount of water, nutrients, and care.
2. Efficient Resource Use
With the help of precision tools, farmers use water, fertilizers, and pesticides more efficiently, reducing waste and cost.
3. Cost Reduction
Automated machines and accurate data help reduce labor costs and minimize input expenses.
4. Environmental Sustainability
By reducing the overuse of chemicals and conserving water, smart farming helps protect the environment and promotes sustainable practices.
5. Better Crop Quality
Monitoring plant health closely leads to the production of healthier crops with better quality and nutritional value.
6. Risk Management
Data analytics and forecasting tools help predict and manage risks like pest attacks, crop diseases, and extreme weather.
7. Labor Management
Automation reduces the need for manual labor and helps overcome labor shortages in rural farming areas.
Challenges in Adopting Smart Farming
1. High Initial Cost
The cost of smart farming equipment and technologies can be expensive for small and marginal farmers.
2. Lack of Awareness and Training
Many farmers are unaware of smart farming technologies or do not have the skills to use them.
3. Poor Internet Connectivity
Smart farming relies on internet-based devices and software. In rural areas, poor connectivity can limit the use of these technologies.
4. Data Privacy Concerns
The use of digital tools raises concerns about the privacy and security of farmers’ data.
5. Maintenance and Support
Smart devices require regular maintenance and technical support, which may not be easily available in all areas.
Future Prospects of Smart Farming
Smart farming has great potential to revolutionize agriculture. With advancements in AI, 5G networks, and automation, smart farming will become more accessible and efficient. Governments and private companies are increasingly investing in agricultural innovation, which will lead to better technologies and wider adoption. Training programs, subsidies, and awareness campaigns can further help farmers embrace smart farming practices.
Conclusion
Smart farming is the future of agriculture. It allows farmers to grow more food with fewer resources while protecting the environment. Though there are challenges in adoption, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. By investing in technology and farmer education, the agricultural sector can become more resilient, profitable, and sustainable. Smart farming is not just a trend; it is a necessary shift toward a more intelligent and efficient food system for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is smart farming in simple terms?
Smart farming uses modern technology like sensors, drones, and data analytics to help farmers monitor crops and livestock more efficiently, reducing waste and improving productivity.
How does smart farming help small farmers?
Smart farming tools can help small farmers monitor weather, soil, and crop conditions with mobile apps and affordable devices, leading to better decisions and higher yields.
What technologies are used in smart farming?
Smart farming includes GPS, IoT sensors, drones, satellite imaging, AI-based tools, and automated irrigation systems that collect data and support precision agriculture.
Is smart farming costly for beginners?
While some tools are expensive, many affordable smart farming apps and sensors are available today. Government schemes and NGOs also help support small-scale farmers.
Related Articles