Our bodies are constantly in a state of flux, taking in nutrients from food and converting them into energy and building blocks for various functions. This intricate process involves two key players: metabolism and nutrient absorption.
Table of Contents
Let’s delve into how these work together to fuel our lives.
Metabolism Defined:
Metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions happening within our cells. It encompasses two main processes:
- Anabolism: The building up of molecules, using energy to create new tissues, repair damaged cells, and synthesize essential compounds.
- Catabolism: The breaking down of molecules to release energy, which is then used to power various bodily functions.
Nutrient Absorption: The Gateway
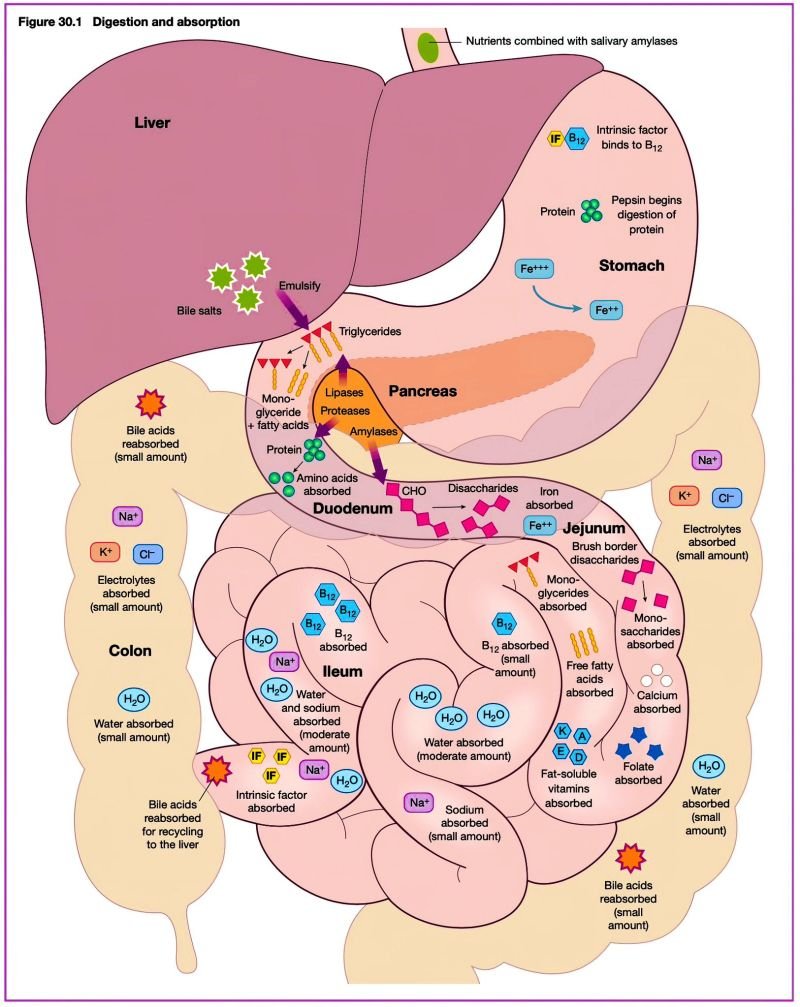
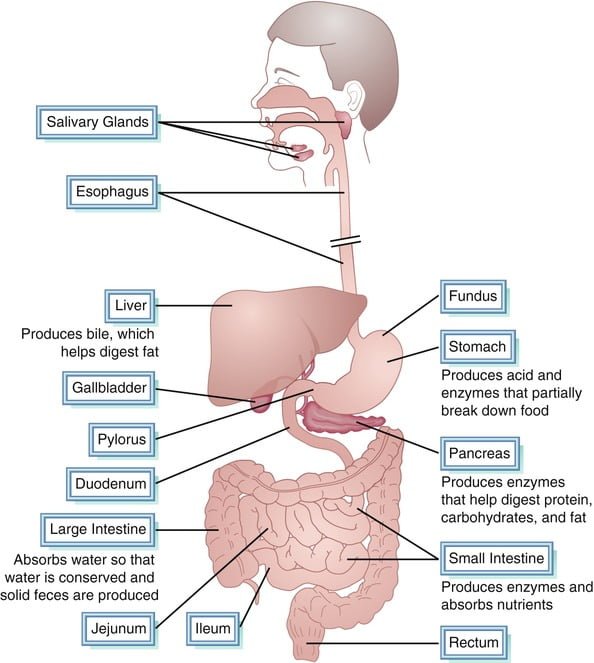
Before metabolism can take center stage, nutrients from food need to enter the bloodstream. This crucial step occurs in the digestive system, specifically the small intestine. Here’s a breakdown of the absorption process:
- Digestion: Food undergoes mechanical and chemical breakdown in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. This breaks down complex molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into simpler forms:
- Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars like glucose.
- Proteins are broken down into amino acids.
- Fats are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Absorption in the Small Intestine: The small intestine, with its vast surface area and finger-like projections called villi, is perfectly suited for nutrient absorption. Here’s where the magic happens:
- Simple sugars: Absorbed directly through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream via facilitated diffusion.
- Amino acids: Transported across the intestinal wall using specific transport proteins.
- Fatty acids and glycerol: Packaged with proteins and cholesterol to form micelles, which are then absorbed by intestinal cells. These fatty molecules are then transported through the lymphatic system before entering the bloodstream.
- Delivery to Cells: Once absorbed, nutrients travel through the bloodstream to reach various body tissues and cells.
The Metabolic Symphony
Now that nutrients have entered the bloodstream, the metabolic orchestra begins its performance:
- Glucose: The primary fuel source for most cells. It enters the cells and undergoes cellular respiration, a process that uses oxygen to generate energy (ATP) for cellular functions.
- Amino Acids: Used for protein synthesis, building and repairing tissues, and creating various hormones and enzymes.
- Fatty Acids: Can be used for immediate energy or stored as triglycerides in adipose tissue for later use. They also play a role in cell membrane structure and signaling.
Regulation and Integration
Metabolism is a tightly regulated process. Hormones like insulin and glucagon work together to maintain blood sugar levels, signaling cells to take up glucose or release it from storage as needed. Similarly, other hormones regulate the utilization of fats and amino acids.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
Providing your body with a balanced diet – rich in carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals – ensures it has the necessary building blocks for optimal metabolism. Deficiencies in any nutrient can disrupt metabolic processes and lead to various health problems.
Additional Points:
- Individual Differences: Metabolic rate, the rate at which your body burns calories, can vary based on factors like age, sex, activity level, and muscle mass.
- Gut Microbiome: Emerging research suggests the gut microbiome, the trillions of microorganisms residing in our intestines, plays a role in nutrient absorption and metabolism.
- Metabolism and Disease: Disruptions in metabolism can contribute to various health conditions like diabetes, obesity, and heart disease.
Comprehending the complex interplay between metabolism and nutrient absorption illuminates how our bodies utilise the food we eat to generate energy and rebuild themselves. We can support ideal metabolic function for a healthy and active life by upholding a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the process of absorption and metabolism?
The mouth, stomach, and small intestine are where digestion takes place. Nutrients are also absorbed in the small intestine and are delivered to our cells through the circulation.
What is nutrient absorption?
Nutrient absorption – This comes after the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, which are essential for energy production, growth, and cellular maintenance.
What is absorption mode of nutrition?
The nutritional substrate (e.g., dead organism or other nonliving organic matter) is directly digested by a variety of enzymes that are excreted by the saprotroph.
Related Articles

