Grasp the nutritional makeup and proper application of different feeds in animal nutrition requires a grasp of feedstuff classification. Feedstuffs are categorised primarily by origin and major nutrient content.
Table of Contents
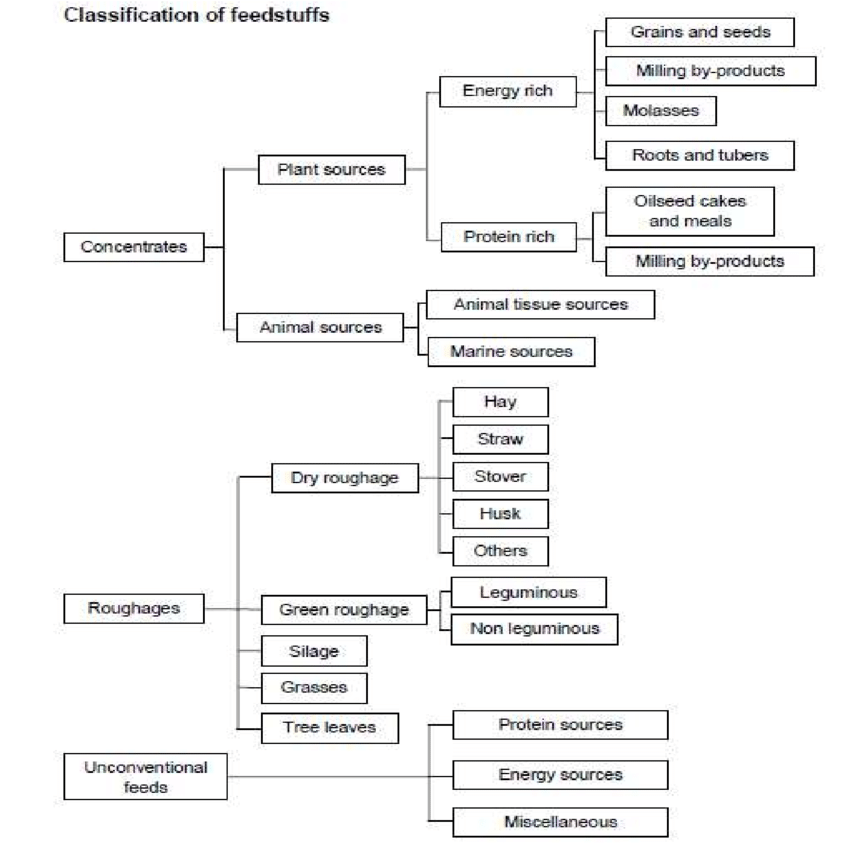
Origin of Feedstuffs
Plant-based:
- Cereals: Corn, wheat, barley, rice, oats, sorghum
- Forages: Hay, silage, pasture, alfalfa
- Oilseeds: Soybean meal, cottonseed meal, rapeseed meal, sunflower meal
- By-products: Brewers grain, distillers grains, citrus pulp, beet pulp

- Animal-based:
- Meat and bone meal: Derived from slaughterhouse waste
- Fish meal: High in protein and essential amino acids
- Milk products: Whey, casein, skim milk powder
- Eggs: Whole eggs, egg yolks, egg whites
- Synthetic:
- Amino acids: Lysine, methionine, tryptophan
- Vitamins: Vitamin A, Vitamin D, Vitamin E
- Minerals: Calcium, phosphorus, magnesium
- Antibiotics: Used for growth promotion and disease prevention
Nutritional Value
- Energy sources: Corn, barley, oats, sorghum, fat
- Protein sources: Soybean meal, cottonseed meal, fish meal, meat and bone meal
- Vitamins and Minerals: Various sources depending on the specific nutrient
- Other: Fiber, water, additives
Physical Form
- Whole:
- Grains: Corn, wheat, barley
- Forages: Hay, silage
- Processed:
- Ground: Corn meal, soybean meal
- Extruded: Pellet form
- Liquid: Molasses, fish oil
Functionality
- Feed ingredients: Grains, oilseeds, forages
- Feed additives:
- Nutritional: Vitamins, minerals, amino acids
- Anti-nutritional factors: Phytate, gossypol
- Performance enhancers: Growth promoters, enzymes
- Sanitary: Antioxidants, mold inhibitors
Animal Species
- Poultry: Corn, soybean meal, wheat, oats
- Swine: Corn, soybean meal, wheat, barley
- Ruminants: Forages, grain by-products, oilseed meals
- Aquaculture: Fish meal, soybean meal, wheat, fish oil
Cost and Availability
- Commodity: Corn, soybean meal, wheat
- Specialty: Fish meal, milk products, synthetic amino acids
Additives
Additives are non-nutritive substances included in feed for various purposes such as enhancing growth, feed efficiency, or animal health.
Examples:
- Antibiotics, probiotics, prebiotics
- Enzymes, antioxidants
- Flavors, colors, preservatives
Non-conventional Feedstuffs
These are alternative feed resources that are not commonly used in traditional feeding programs but can be valuable under specific conditions.
Examples:
- Agro-industrial by-products (brewer’s grains, citrus pulp, sugar beet pulp)
- Unconventional grains (sorghum, millet)
- Novel protein sources (insect meal, algae)
Special Feeds
Special feeds are designed for specific purposes or stages of production.
Examples:
- Milk replacers for young animals
- Lactation feeds for dairy cows
- Finishing feeds for meat animals
Example of a Feedstuff Classification
Feedstuff: Corn
- Origin: Plant-based, Cereal
- Nutritional Value: Energy source
- Physical Form: Whole, Ground
- Functionality: Feed ingredient
- Animal Species: Poultry, swine, ruminants
- Cost and Availability: Commodity

Important Considerations
- Digestibility: The extent to which nutrients are absorbed by the animal.
- Palatability: The taste and acceptance of the feedstuff by the animal.
- Safety: The absence of toxins or contaminants.
- Storage: The conditions required to maintain the quality of the feedstuff.
The classification of feedstuffs helps in formulating balanced diets that meet the nutritional needs of different animal species and production stages. Understanding the characteristics of each category ensures the efficient and economical use of available feedstuffs resources.
By understanding the different classifications of feedstuffs, animal producers can make informed decisions about the ingredients they use to formulate diets that meet the specific nutritional needs of their animals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the meaning of feedstuffs?
Any material used as a food, esp for animals. A feedstuff is a component of a ration or a diet that serves one or more functions. The functions of a feedstuff can be divided into two categories. The first category is the feedstuff provides one or more of the six essential nutrients.
What are the classification of Roughages?
Roughages come in three primary forms: pastures, silages, and dry roughages. Hay, straw, and chemically dehydrated forages—which comprise roughly 90% dry matter—are examples of dry roughages.
What are two examples of feedstuffs high in protein?
Soy and fishmeal are 2 of the main ingredients used to meet animals’ protein requirements in feed rations because they provide substantial levels of protein and essential amino acids.
Related Articles

