Agricultural project planning involves organizing and outlining the steps and resources necessary to successfully execute an agricultural initiative. The aim is to ensure the project is efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable. Whether you’re starting a small farm or managing a large agribusiness, a well-developed plan is essential for securing funding, managing resources, and guiding the project from start to finish.
Agricultural projects can take various forms, such as crop production, livestock farming, or agribusiness ventures like food processing. Each type of project requires specific strategies, resources, and timelines, which must be clearly defined during the planning process.
Table of Contents
Types of Agricultural Projects
Crop Production

Projects focused on cultivating crops for food, fiber, or other products. These crops depend on the region, climate, and market demand, and can include cereals like wheat or rice, vegetables, fruits, or cash crops like coffee and cotton. Planning for these projects requires consideration of land use, irrigation, fertilizers, pest control, and harvest schedules.
Livestock Farming
These projects involve raising animals like cattle, sheep, poultry, or fish for meat, milk, eggs, or other purposes such as wool or leather. Key considerations in livestock farming include housing, feeding, veterinary care, breeding, and waste management, along with disease control and biosecurity.

Agro-processing
These projects aim to transform raw agricultural products into finished goods, such as turning milk into cheese or processing fruit into juice. Adding value to farm products can increase revenue. Planning involves setting up processing facilities, ensuring a steady supply of raw materials, managing logistics, and following food safety regulations.
Agroforestry
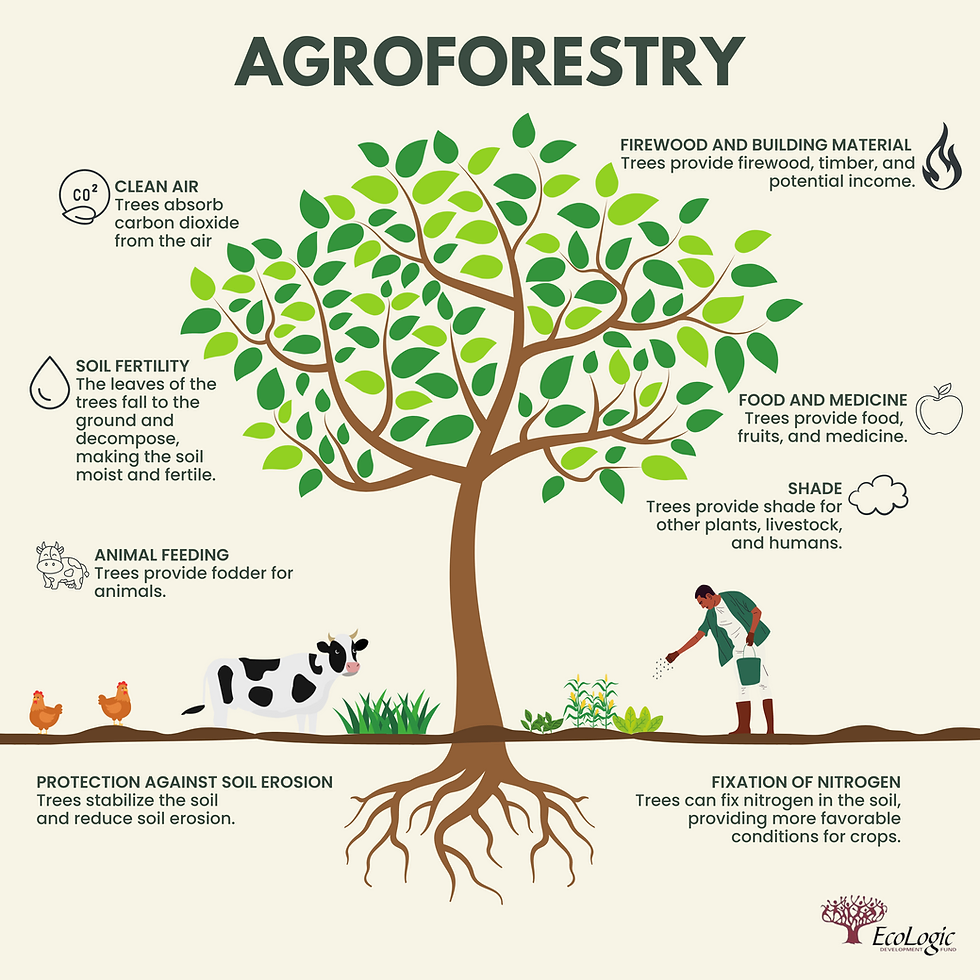
This type of project combines agriculture and forestry by growing trees alongside crops or livestock on the same land. Agroforestry helps to improve biodiversity, conserve water, and prevent soil erosion. Effective planning involves careful land management, tree species selection, and sustainable long-term practices.
Agritech
Agritech projects involve using technology to enhance farming practices, such as precision agriculture, drones for crop monitoring, or digital platforms to connect farmers with markets. These projects require planning that integrates modern tools and technologies to improve efficiency and productivity.
Methods of Agricultural Project Planning
Effective agricultural project planning requires a structured approach to cover all necessary components. Here are several methods used in the planning process:
1. Participatory Planning
In participatory planning, all stakeholders—such as farmers, community members, and government agencies—actively participate in the project’s development. This method incorporates local knowledge, experiences, and needs to create a plan that is more sustainable and inclusive. It is particularly useful for community-based projects that depend on collaboration.
2. Top-down Planning
In top-down planning, a central authority such as a government agency or large company makes the key decisions regarding the project. They establish the goals, allocate resources, and oversee progress. This method is effective in large-scale projects where fast decision-making and strict management are required but may lack local insight.
3. Bottom-up Planning
Bottom-up planning begins at the grassroots level, where local farmers or stakeholders develop project ideas and goals, which are then supported by higher authorities. This method ensures that the project reflects the real needs of the community, fostering ownership among participants and often leading to more sustainable results.
4. Project Cycle Management (PCM)
PCM is a method that manages projects through their entire lifecycle. It consists of several stages:
Identification: Defining the project’s goals and target beneficiaries.
Planning and Design: Developing a detailed plan, timeline, and budget.
Implementation: Executing the plan and monitoring progress.
Evaluation: Assessing the project’s success and identifying lessons for the future. PCM ensures that each phase of the project is thoroughly planned and managed, reducing the risk of failure.
5. Logical Framework Approach (Logframe)
The Logframe method breaks the project down into logical steps, each with defined objectives, activities, and success indicators. A Logframe typically includes:
Objectives: What the project aims to achieve.
Activities: Specific tasks that will be completed.
Outputs: The immediate results of these activities.
Outcomes: The broader changes the project is targeting. This method is commonly used by development organizations and NGOs to manage agricultural projects effectively.
6. SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
SWOT analysis helps project planners identify internal and external factors that could affect the project. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses within the project, as well as the opportunities and threats from external sources, planners can develop strategies to increase success and reduce risks.
Conclusion
Agricultural project planning is vital for the successful execution of farming or agribusiness initiatives. It involves setting clear objectives, managing resources, and establishing a structured plan tailored to the specific type of agriculture being pursued. By using methods such as participatory planning, PCM, Logframe, or SWOT analysis, project planners can create well-organized, sustainable, and efficient plans. Whether the project is community-based or high-tech, proper planning is crucial for long-term success and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is agricultural project planning?
Agricultural project planning involves outlining the necessary steps, resources, and strategies to implement a farming or agribusiness initiative successfully. It covers everything from setting objectives to managing resources and timelines.
What is the top-down approach in agricultural project planning?
The top-down approach in agricultural project planning, decisions and strategies are made by a central authority, such as government bodies or corporate organizations. The central authority controls the planning and execution, and this method is usually employed in large-scale projects requiring efficient, fast decision-making.
What is SWOT analysis in agricultural project planning?
SWOT analysis in agricultural project planning are strength, weakness, opportunities and threats.
Related Articles

