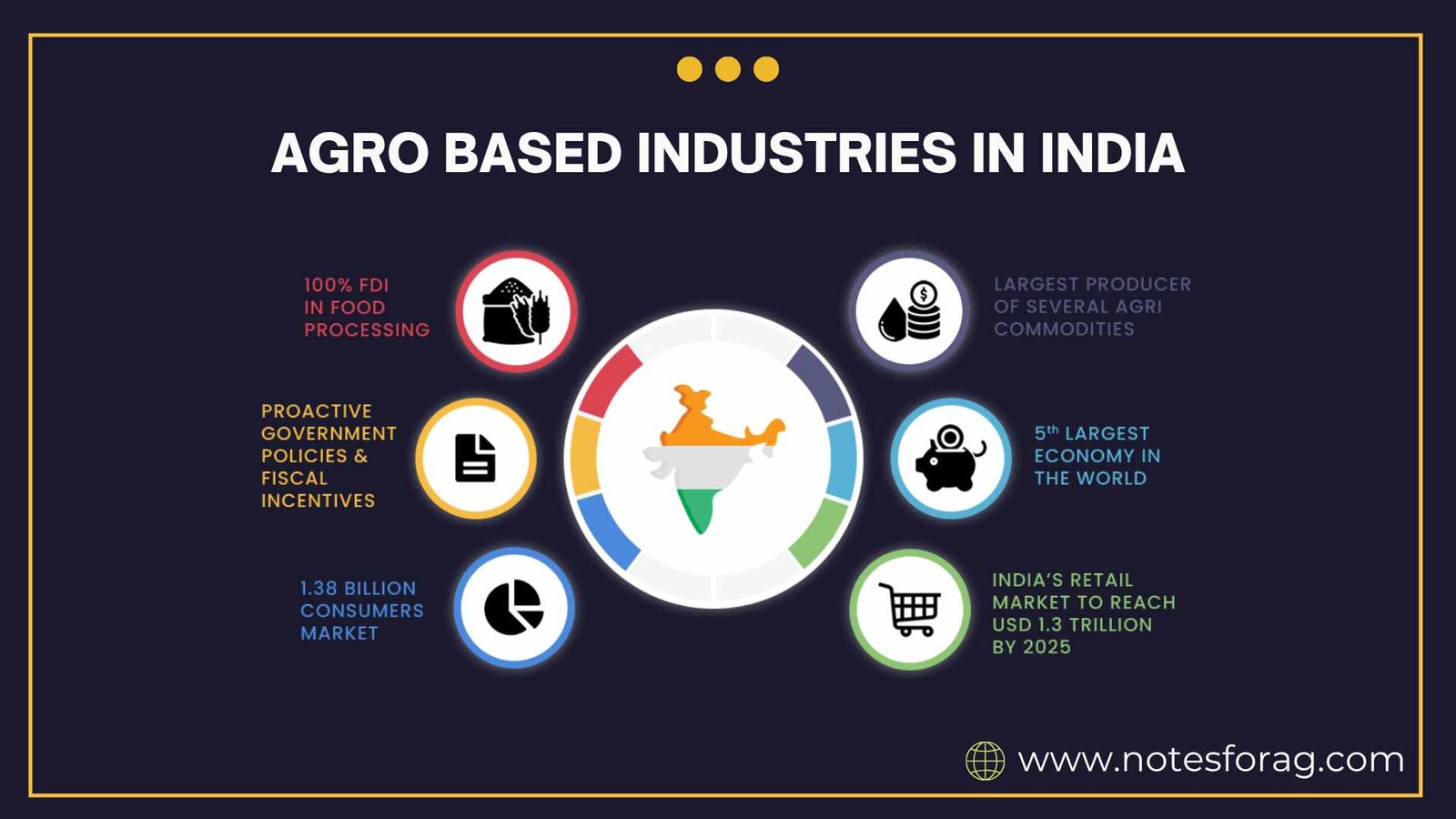
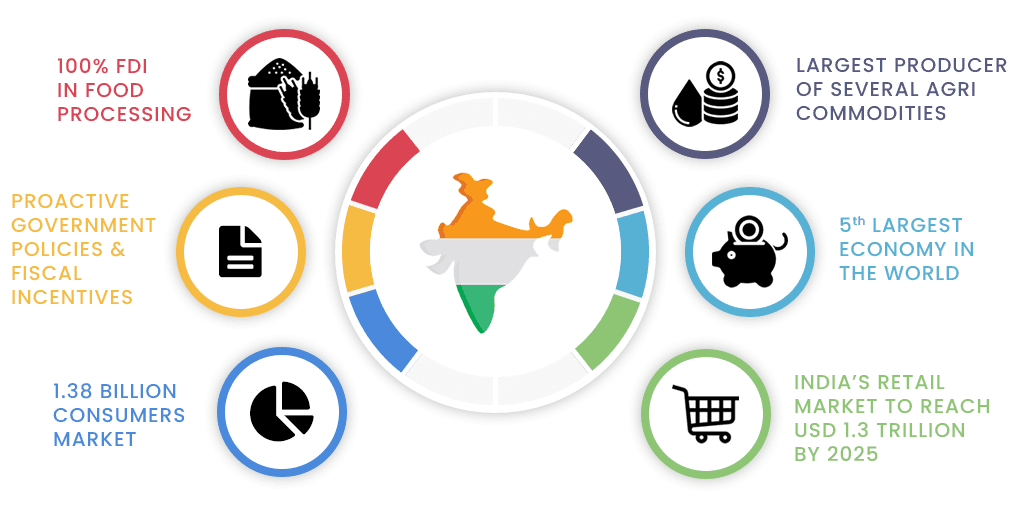
INTRODUCTION TO AGRO BASED INDUSTRIES
Agro based industries in India form a crucial link between agriculture and industry, providing employment, enhancing value addition, and promoting rural development. These industries primarily use agricultural raw materials for manufacturing goods, thus playing a significant role in boosting the rural economy. With India being one of the world’s largest producers of agricultural products, agro based industries have immense potential for growth and diversification.
Summary of Agro Based Industries
- India’s agro‑based industries process agricultural raw materials like food, textiles, dairy, and biofuels, transforming them into value‑added products that boost rural income and reduce wastage .
- Key sectors include food processing, textiles, dairy, sugar, edible oils, tea, coffee, leather, biofuels, and paper, each contributing to employment, exports, and regional development .
- Despite infrastructure, finance, and regulatory challenges, government support through schemes like PM‑FME, Mega Food Parks, and NABARD funding is expanding industry growth .
Table of Contents
TYPES OF AGRO BASED INDUSTRIES
1. Food Processing Industry
The food processing industry includes all operations from the harvesting of raw materials to the final consumption of the processed product. It involves drying, packaging, canning, freezing, and preserving food.
Importance
This industry reduces post-harvest losses, increases shelf life, ensures food safety, and meets consumer demand for ready-to-eat food.
Examples
Fruit and vegetable processing, dairy products, meat and fish processing, and bakery goods.
2. Textile Industry
The textile industry is one of the oldest agro based industries in India, relying heavily on cotton, jute, wool, and silk for its raw materials.
Importance
It contributes significantly to employment, exports, and industrial production in India.
Examples
Cotton spinning and weaving mills, jute mills, and silk production units.
3. Sugar Industry

India is the second-largest producer of sugar in the world. The sugar industry is crucial for the rural economy and operates mainly in states like Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Karnataka.
Importance
It provides employment to millions of farmers and factory workers and contributes to ethanol production.
By-products
Molasses, bagasse, and press mud are used in alcohol production, power generation, and as fertilizers.
4. Dairy Industry
The dairy industry in India has grown remarkably under Operation Flood. It includes milk production, collection, processing, packaging, and distribution.
Importance
It ensures food security, provides nutrition, and offers income opportunities, especially for small and marginal farmers.
Examples
Milk cooperatives, cheese and butter production, and ice cream factories.
5. Edible Oil Industry
India imports a large portion of its edible oil despite being a major oilseed producer. The edible oil industry processes oilseeds like groundnut, mustard, soybean, and sunflower.
Importance
It supports oilseed farmers and reduces dependency on imports.
Examples
Mustard oil mills, groundnut oil extraction units, and solvent extraction plants.
6. Tea, Coffee, and Spices Industry
India is known for its premium quality tea, coffee, and spices, with specific regions specialized in their cultivation.
Importance
These are major export commodities that bring foreign exchange and promote regional development.
Examples
Tea estates in Assam, coffee plantations in Karnataka, and spice processing units in Kerala.
7. Tobacco Industry

The tobacco industry includes the cultivation, processing, and manufacture of products such as cigarettes, bidis, and chewing tobacco.
Importance
It contributes significantly to revenue through taxation and exports.
Concerns
Health concerns related to tobacco consumption have led to regulatory restrictions.
8. Paper and Pulp Industry
This industry utilizes agro-residues like bagasse, bamboo, and wood pulp.
Importance
It supports sustainable development by using agricultural waste and generating employment in rural areas.
Examples
Newsprint mills, packaging paper units, and eco-friendly paper producers.
9. Leather Industry
The leather industry uses hides and skins from animals, often sourced from slaughterhouses linked to the meat industry.
Importance
It is a major export-oriented industry offering jobs in tanning, manufacturing, and designing leather goods.
Examples
Footwear factories, leather garment units, and leather accessories production.
10. Biofuel and Biogas Industry
Biofuel industries use crops like sugarcane, maize, and agricultural waste to produce ethanol and biodiesel.
Importance
They help reduce fossil fuel dependency and promote renewable energy.
Examples
Biogas plants, ethanol distilleries, and biodiesel manufacturing units.
ROLE OF AGRO BASED INDUSTRIES IN INDIAN ECONOMY
1. Employment Generation
Agro-industries are labor-intensive and provide employment to millions of people, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas.
2. Value Addition
They add value to agricultural products through processing, thereby increasing farmers’ income and contributing to GDP.
3. Rural Development
Agro-industries promote infrastructure development, entrepreneurship, and social upliftment in rural regions.
4. Export Promotion
Many agro-industrial products are exported, contributing to foreign exchange earnings.
5. Balanced Regional Growth
They help decentralize industrial development and reduce pressure on urban areas by promoting industries in rural zones.
CHALLENGES FACED BY AGRO BASED INDUSTRIES
1. Raw Material Shortages
Inconsistent supply and quality of raw materials due to climatic or logistic issues.
2. Lack of Modern Technology
Many small-scale units lack access to modern processing technologies and machinery.
3. Poor Infrastructure
Insufficient cold storage, transport, and energy supply limit the efficiency of agro-industries.
4. Financial Constraints
Limited credit facilities and high interest rates discourage investment in agro-processing.
5. Regulatory Hurdles
Complicated licensing, pollution control norms, and export restrictions affect ease of doing business.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES AND SUPPORT FOR AGRO BASED INDUSTRIES IN INDIA
1. PM FME Scheme (Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises)
Helps micro-enterprises become formalized and provides financial support and training.
2. Mega Food Parks Scheme
Creates well-equipped processing clusters with modern infrastructure.
3. National Mission on Food Processing
Provides grants for capacity building, technology adoption, and cold chain development.
4. Startup India and Atmanirbhar Bharat
Promotes agri-startups and self-reliance in food and energy sectors.
5. Interest Subsidies and Tax Benefits
Special financial schemes to support agro-processing industries in backward and rural areas.
FUTURE PROSPECTS OF AGRO BASED INDUSTRIES IN INDIA
Agro based industries have a bright future owing to rising domestic and global demand for processed food, textiles, and bio-products. With improvements in infrastructure, digital marketing, export facilitation, and public-private partnerships, these industries are expected to contribute more significantly to GDP and rural transformation. Emphasis on organic products, eco-friendly packaging, and climate-resilient technologies will shape the future of agro-industrial development in India.
CONCLUSION
Agro-based industries are an essential part of India’s economy. They create a strong link between agriculture and industrial development, helping farmers and rural communities grow.
These industries add value to raw agricultural products by processing them into finished goods. This process increases farmers’ income and reduces wastage of crops.
Employment generation is another major benefit. Agro industries provide jobs to millions, especially in rural areas where alternative opportunities are limited.
Agro-based industries also help promote balanced regional development. By encouraging industrial growth in rural areas, they reduce pressure on cities and improve infrastructure in less developed regions.
The government has recognized the importance of these industries and introduced various schemes such as PM-FME and Mega Food Parks to support growth. Financial aid, technology support, and policy reforms are helping small and medium agro enterprises flourish.
Despite their potential, these industries face challenges like raw material shortages, outdated technology, poor infrastructure, and regulatory hurdles. Addressing these issues is crucial for sustainable growth.
Looking ahead, the future of agro-based industries in India appears promising. Increasing demand for processed food, textiles, biofuels, and organic products will drive expansion.
Integration of modern technologies, digital marketing, and eco-friendly practices will further boost productivity and market reach. Export opportunities will also grow, bringing more foreign exchange to the country.
In summary, agro-based industries are vital for inclusive growth, rural prosperity, and economic resilience. With continued government support and innovation, they can transform India’s agricultural landscape and strengthen the economy for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are agro based industries?
Agro based industries are industries that use agricultural raw materials like crops, fruits, and livestock products to manufacture goods. They add value to farm produce and help in rural development.
Which is not the agro based industry?
An industry that does not use agricultural raw materials as its primary input is not an agro based industry. For example, the steel or textile industry is not agro based.
Which government initiatives support agro‑based industries?
Key programs include PM‑FME for small enterprises, Mega Food Parks for infrastructure, National Mission on Food Processing, Startup India, and NABARD credit schemes.
What is the future outlook for agro‑based industries in India?
With rising demand, digital tech integration, eco-friendly packaging, and focus on exports, agro‑based industries are poised for growth and rural transformation.
Related Articles