The food we eat has a big impact on our health, especially when it comes to degenerative diseases chronic conditions that get worse over time. Our diets can play a big role in either helping protect us from these diseases or increasing our risk of them. Here’s a simple look at how diets impact different degenerative diseases.
Table of Contents
1. Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
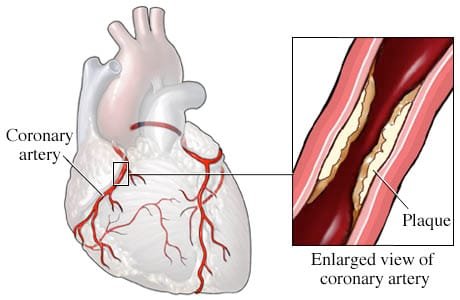
What is CHD?
It’s a condition where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged with fatty deposits, which can lead to chest pain or even a heart attack.
How Diet Affects CHD: Diets high in unhealthy fats (like saturated and trans fats) and added sugars can increase cholesterol and blood pressure, raising the risk of clogged arteries.
Diet Choices to Help Prevent CHD: Eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can reduce the risk. Foods high in omega-3s (like salmon and walnuts) can also help lower cholesterol and reduce inflammation. Reducing salt by avoiding processed foods can also help manage blood pressure.
2. Diabetes Mellitus

What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition where blood sugar stays too high due to problems with insulin. In Type 2 diabetes, the body doesn’t use insulin properly, often due to lifestyle factors.
How Diet Affects Diabetes: Diets high in refined sugars and processed foods can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of Type 2 diabetes. Foods that cause blood sugar spikes (like white bread and sugary drinks) put stress on the insulin system.
Diet Choices to Help Prevent Diabetes: A diet rich in whole foods, especially whole grains, fiber, and lean proteins, can help stabilize blood sugar. Reducing processed foods and focusing on vegetables, legumes, and nuts provides steady energy without causing blood sugar spikes.
3. Cancer
What is Cancer?
Cancer is the abnormal growth of cells that can spread throughout the body. Diet is one of the factors that can influence cancer risk.
How Diet Affects Cancer: Diets high in processed and red meats, sugary foods, and unhealthy fats may increase cancer risk by promoting inflammation and oxidative stress. High-fat diets and alcohol are also linked to cancer growth.
Diet Choices to Help Prevent Cancer: Eating lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides antioxidants, fiber, and plant compounds that can protect against cancer. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli contain compounds that neutralize cancer-causing substances. Limiting alcohol, sugar, and choosing lean protein sources can also help.
4. Gastrointestinal Problem
What are GI Problems?
Digestive issues like acid reflux, IBS, and constipation affect the stomach and intestines and can lead to chronic health problems.
How Diet Affects GI Problems: Low fiber can lead to constipation, while fatty and spicy foods can worsen acid reflux. People with IBS may also react to specific foods that irritate their digestion.
Diet Choices to Help GI Health: Increasing fiber intake from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables promotes regular digestion. Fermented foods like yogurt and sauerkraut contain beneficial bacteria that support gut health. Avoiding fatty, spicy, and large meals can reduce acid reflux.
5. Renal Disorders (Kidney Diseases)
What are Kidney Disorders?
Kidney disease affects the kidneys’ ability to filter waste, leading to toxin buildup in the body.
How Diet Affects Kidney Health: Diets high in sodium and processed foods can put stress on the kidneys. When kidneys can’t filter sodium and waste properly, blood pressure increases, worsening kidney function.
Diet Choices to Help Kidney Health: Reducing sodium by avoiding processed foods and choosing fresh, whole ingredients can protect kidney health. In advanced kidney disease, limiting protein may also be necessary. Staying hydrated and monitoring potassium intake is helpful, depending on the condition.
6. Urolithiasis (Kidney Stones)
What are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are mineral deposits that form in the kidneys and cause pain when they move through the urinary tract.
How Diet Affects Kidney Stones: A diet high in oxalates (like spinach and nuts), salt, and low water intake can lead to kidney stones. Low water intake concentrates minerals, making stones more likely.
Diet Choices to Help Prevent Kidney Stones: Drinking lots of water is the best way to prevent kidney stones. Reducing salt and oxalate-rich foods (like spinach) and limiting animal protein can also help.
7. Food and Cataracts
What are Cataracts?
Cataracts are a clouding of the eye lens that makes vision blurry. Diet can influence cataract risk over time.
How Diet Affects Cataracts: Diets low in antioxidants can increase cataract risk, as antioxidants help protect eye cells from damage by free radicals.
Diet Choices to Help Prevent Cataracts: Eating foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, citrus fruits, and leafy greens, may reduce the risk. Vitamins A, C, and E are especially good for eye health, as they help protect the eyes from free radical damage.
Conclusion
Eating a balanced diet of fresh, whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help protect against degenerative diseases. By choosing these foods over processed foods with added sugars, unhealthy fats, and salt, we can lower the risk of chronic conditions. Making healthy dietary choices is a powerful way to support long-term health and reduce the risk of these diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a balanced diet?
A balanced diets includes a variety of foods that provide all essential nutrients in the right proportions. It typically consists of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a moderate amount of dairy or dairy alternatives.
Can diet affect sleep quality?
Yes, diets affect sleep. Caffeine, large meals before bedtime, and heavy, fatty foods can disrupt sleep. Foods rich in magnesium (like nuts, leafy greens, and bananas) and foods with tryptophan (like turkey and dairy) can promote relaxation and better sleep.
Related Articles

