Education pathways is a diverse process that is critical to society development. It includes formal, informal, and non-formal approaches. Formal education takes place in structured institutions such as schools and universities, where students gain systematic information and accredited degrees. Informal education occurs through everyday encounters, promoting lifelong learning and cultural transmission in the absence of a prescribed curriculum. Non-formal education refers to structured learning activities that take place outside of traditional institutions, such as community programs and vocational training, with the goal of meeting unique educational requirements and encouraging social participation.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Education Pathways
Education pathways, in its broadest definition, refers to the different ways in which people acquire knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes. There are three types of education pathways in society: official, informal, and non-formal education. Each of these education pathways is critical to promoting individual growth and society development.
Formal education is the systematic system of learning that occurs in schools, colleges, and universities. It is distinguished by a well-defined curriculum, standardized assessment systems, and qualified teachers. This sort of education often results in recognized certificates and degrees, which are required for professional advancement and personal development.
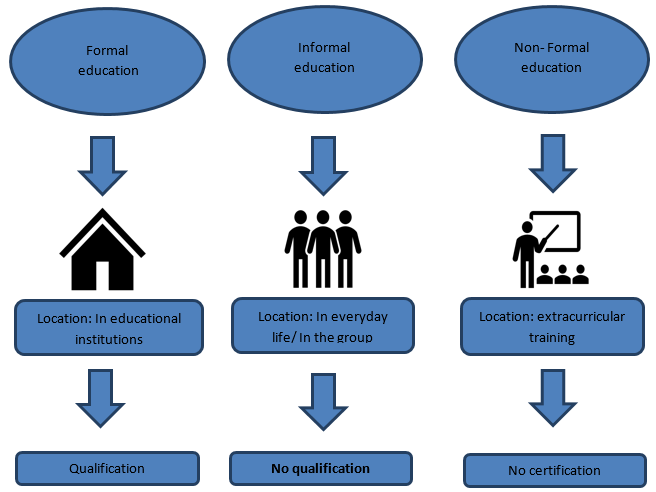
In contrast, informal education takes place outside of formal educational institutions and is not limited to a certain curriculum or organization. It encompasses learning through daily activities, relationships with family and classmates, and exposure to media and technology. Informal education is frequently spontaneous and motivated by the learner’s interests and requirements, allowing them to gain practical skills and knowledge in a more flexible and individualized setting.
Non-formal education falls between formal and informal education. It is planned and systematic, but it does not always follow a strict curriculum or result in formal certification. Non-formal education includes adult education programs, community-based workshops, and vocational training courses.
Formal Education
Formal education is a systematic and structured form of learning that typically takes place in schools, colleges, and universities. Governed by state policies and educational standards, formal education follows a standardized curriculum designed to impart knowledge and skills in a sequential manner.
Nature
- Structured and Systematic: Delivered in a formal context, such as schools, colleges, or universities.
- Certified: Leads to recognized credentials such as certificates and degrees.
- Curriculum-Based: Follows a predetermined curriculum and established testing techniques.
Role
- Skill Development: Provides individuals with necessary skills and information for professional vocations.
- Socialization: Teaches societal standards, morals, and cultural understanding.
- Economic Contribution: Increases employability and economic output.
Characteristics
- Institutionalized: Conducted in recognized institutes.
- Teacher-Led: Professional educators deliver the content.
- Progressive: There is a hierarchical system that runs from primary to higher education.
Informal Education
Informal education transcends the boundaries of traditional classroom settings, occurring organically through daily interactions, experiences, and activities. This form of education is deeply embedded in the fabric of society, manifesting in diverse contexts such as family teachings, peer discussions, and community involvement.
Nature
- Unstructured and spontaneous: It happens spontaneously through ordinary events.
- No formal certification: Lacks formal recognition and credentials.
Role
- Life Skills: Encourages the development of practical skills through real-world experiences.
- Cultural Transmission: Passes on traditions, ideals, and cultural behaviors.
- Lifelong Learning: Promotes constant personal development and adaptation.
Characteristics
- Flexible: Adapts to individual requirements and conditions.
- Non-institutional: Occurs outside of typical educational settings.
- Self-Directed: Typically prompted by the student.
Non-Formal Education
Non-formal education represents an essential component of the educational landscape, providing organized learning experiences that diverge from the structured curriculum of formal education systems.
Nature
- Organized, but flexible: Structured learning experiences outside of the conventional school system.
- Variable Certification: Certificates or credentials may be issued depending on the program.
Role
- Skill Improvement: Provides additional skills and knowledge that are not addressed in traditional schooling.
- Community development: Provides specialized training and education to local communities.
- Bridging gaps: Provides educational opportunities for underprivileged or underserved groups.
Characteristics
- Program-Based: Includes workshops, vocational training, and adult education.
- Participant-Centered: Tailored to the needs and interests of the learners.
- Diverse Settings: Can take place in community centers, workplaces, or online venues.
Non-formal education supports both formal and informal education, contributing to a more comprehensive approach to learning. While formal education gives basic information and informal education promotes self-directed discovery, non-formal education bridges the gap by providing structured yet adaptable learning experiences. This collaboration enables a holistic educational path that can adapt to the changing requirements of society and individuals alike.
Education pathways, including formal, informal, and non-formal education, all play important roles in personal and societal development. Formal education offers structured learning and recognized qualifications, whereas informal education promotes lifetime learning via everyday experiences, and non-formal education targets unique needs and practical skills outside of established institutions. Together, these pathways form a holistic educational environment that meets varied learning requirements, promotes community development, and contributes to individual and societal advancement.
Frequently Asked Question(FAQ)
What is formal education?
Formal education refers to the structured and systematic learning that occurs in institutions such as schools, colleges, and universities. It follows a predetermined curriculum, leads to recognized certificates or degrees, and is typically provided by qualified educators.
What is informal education?
Informal education takes place outside of formal institutional contexts and involves spontaneous, unstructured learning from daily events, interactions, and activities. Examples include learning from family, friends, hobbies, and professional experiences.
What is non-formal education?
Non-formal education refers to structured learning activities that are not part of the regular educational system. It is frequently adaptable, elective, and intended to address specific learning needs or goals. Examples include community seminars, adult education classes, and vocational training programs.
Related Articles

